publications
Full publications on Google Scholar. Asterisk (*) means equal contribution.
2025
-
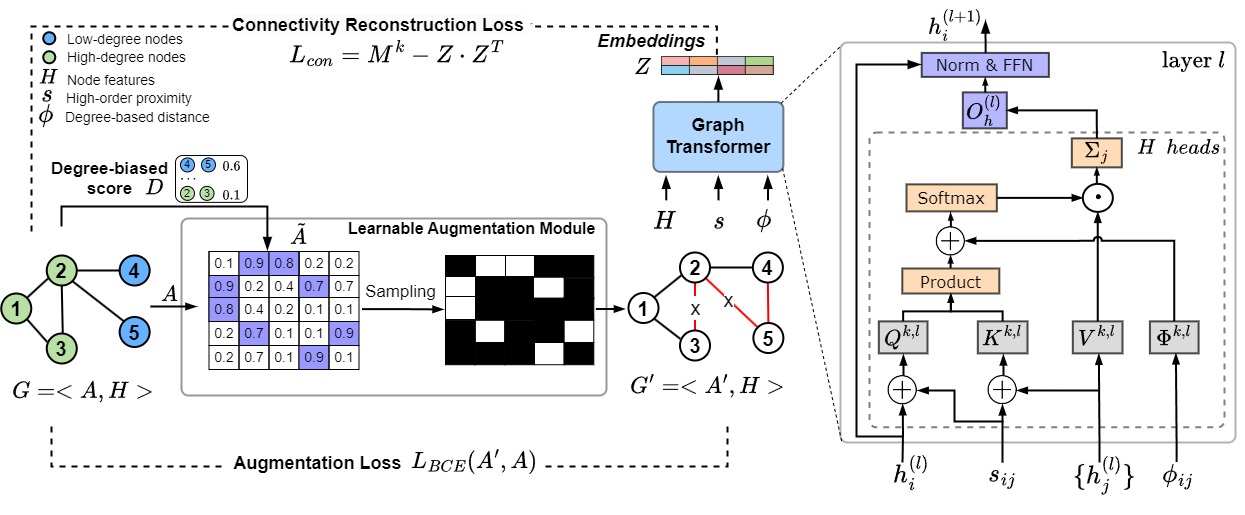 Mitigating Degree Bias in Graph Representation Learning With Learnable Structural Augmentation and Structural Self-AttentionVan Thuy Hoang, Hyeon-Ju Jeon , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2025
Mitigating Degree Bias in Graph Representation Learning With Learnable Structural Augmentation and Structural Self-AttentionVan Thuy Hoang, Hyeon-Ju Jeon , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2025Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) update node representations through message passing, which is primarily based on the homophily principle, assuming that adjacent nodes share similar features. However, in real-world graphs with long-tailed degree distributions, high-degree nodes dominate message passing, causing a degree bias where low-degree nodes remain under-represented due to inadequate messages. The main challenge in addressing degree bias is how to discover non-adjacent nodes to provide additional messages to low-degree nodes while reducing excessive messages for high-degree nodes. Nevertheless, exploiting non-adjacent nodes to provide valuable messages is challenging, as it could generate noisy information and disrupt the original graph structures. To solve it, we propose a novel Degree Fairness Graph Transformer, named DegFairGT, to mitigate degree bias by discovering structural similarities between non-adjacent nodes through learnable structural augmentation and structural self-attention. Our key idea is to exploit non-adjacent nodes with similar roles in the same community to generate informative edges under our augmentation, which could provide informative messages between nodes with similar roles while ensuring that the homophily principle is maintained within the community. By considering the structural similarities among non-adjacent nodes to generate informative edges, DegFairGT can overcome the imbalanced messages while still preserving the graph structures. To enable DegFairGT to learn such structural similarities, we then propose a structural self-attention to capture the similarities between node pairs. To preserve global graph structures and prevent graph augmentation from hindering graph structure, we propose a Self-Supervised Learning task to preserve p-step transition probability and regularize graph augmentation. Extensive experiments on six datasets showed that DegFairGT outperformed state-of-the-art baselines in degree fairness analysis, node classification, and node clustering tasks. © 2013 IEEE.
-
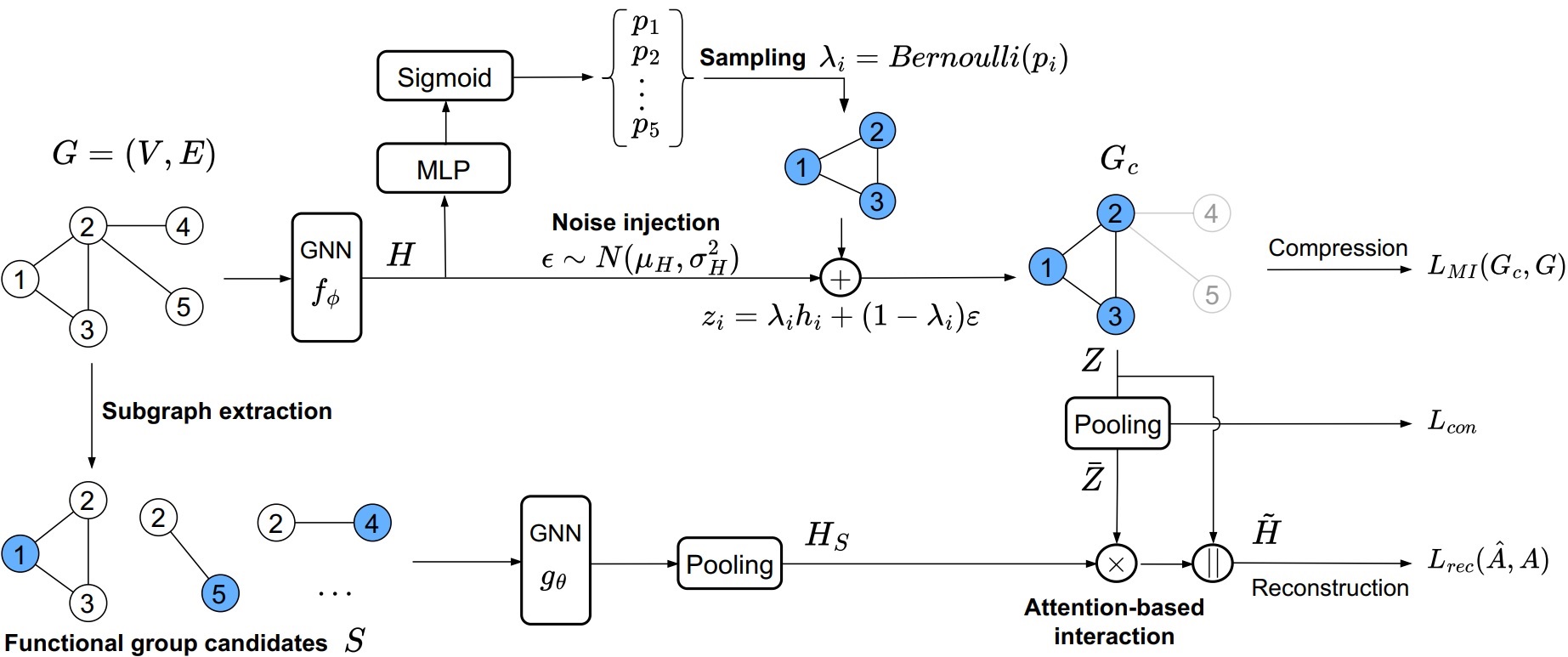 Pre-Training Graph Neural Networks on Molecules by Using Subgraph-Conditioned Graph Information BottleneckVan Thuy Hoang , and O-Joun LeeIn Proceedings of the 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025) , 2025
Pre-Training Graph Neural Networks on Molecules by Using Subgraph-Conditioned Graph Information BottleneckVan Thuy Hoang , and O-Joun LeeIn Proceedings of the 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025) , 2025This study aims to build a pre-trained Graph Neural Network (GNN) model on molecules without human annotations or prior knowledge. Although various attempts have been proposed to overcome limitations in acquiring labeled molecules, the previous pre-training methods still rely on semantic subgraphs, i.e., functional groups. Only focusing on the functional groups could overlook the graph-level distinctions. The key challenge to build a pre-trained GNN on molecules is how to (1) generate well-distinguished graph-level representations and (2) automatically discover the functional groups without prior knowledge. To solve it, we propose a novel Subgraph-conditioned Graph Information Bottleneck, named S-CGIB, for pre-training GNNs to recognize core subgraphs (graph cores) and significant subgraphs. The main idea is that the graph cores contain compressed and sufficient information that could generate well-distinguished graph-level representations and reconstruct the input graph conditioned on significant subgraphs across molecules under the S-CGIB principle. To discover significant subgraphs without prior knowledge about functional groups, we propose generating a set of functional group candidates, i.e., ego networks, and using an attention-based interaction between the graph core and the candidates. Despite being identified from self-supervised learning, our learned subgraphs match the real-world functional groups. Extensive experiments on molecule datasets across various domains demonstrate the superiority of S-CGIB. Copyright © 2025, Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved.
-
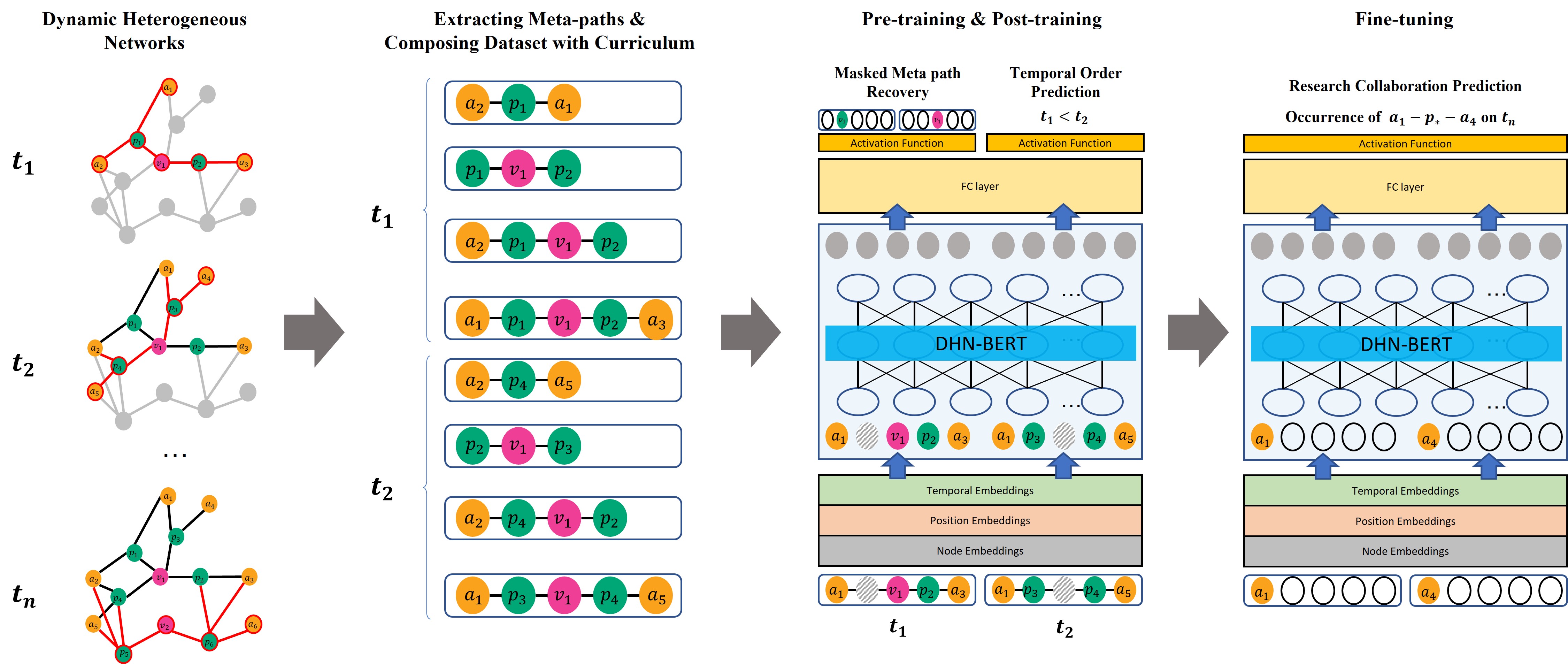 Curriculum-Guided Self-Supervised Representation Learning of Dynamic Heterogeneous NetworksNamgyu Jung, David Camacho , Chang Choi , and O-Joun LeeCognitive Computation, 2025
Curriculum-Guided Self-Supervised Representation Learning of Dynamic Heterogeneous NetworksNamgyu Jung, David Camacho , Chang Choi , and O-Joun LeeCognitive Computation, 2025Since most real-world network data include nodes and edges that evolve gradually, an embedding model for dynamic heterogeneous networks is crucial for network analysis. Transformer models have remarkable success in natural language processing but are rarely applied to learning representations of dynamic heterogeneous networks. In this study, we propose a new transformer model (DHG-BERT) that (i) constructs a dataset based on a network curriculum and (ii) includes pre/post-learning through self-supervised learning. Our proposed model learns complex relationships by leveraging an easier understanding of relationships through data reconstruction. Additionally, we use self-supervised learning to learn network structural features and temporal changes in structure and then fine-tune the proposed model by focusing on specific meta-paths by considering domain characteristics or target tasks. We evaluated the quality of the vector representation produced by the proposed transducer model using real bibliographic networks. Our model achieved an average accuracy of 0.94 in predicting research collaboration between researchers, outperforming existing models by a minimum of 0.13 and a maximum of 0.35. As a result, we confirmed that DHG-BERT is an effective transformer model tailored to dynamic heterogeneous network embeddings. Our study highlights the model’s ability to understand complex network relationships and appropriately capture the structural nuances and temporal changes inherent in networks. This study provides future research directions for applying the transformer model to real-world network data and a new approach to analyzing dynamic heterogeneous networks using transformers. © The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2025.
- IEEE AccessA Comparative Study of Deep Audio Models for Spectrogram- and Waveform-Based SingFake DetectionMinh Nguyen-Duc , Luong Vuong Nguyen, Huy Nguyen-Ho-Nhat , Tri-Hai Nguyen , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2025
Recent advancements in singing voice synthesis have significantly improved the quality of artificial singing voices, raising concerns about their potential misuse in generating deepfake singing, or “singfake” voices. Detecting these synthetic voices presents unique challenges due to the complex nature of singing, which involves pitch, timbre, and accompaniment variations. In this study, we conduct a comparative analysis of two model types for singfake detection: (1) models utilizing Log-Mel spectrograms, such as Audio Spectrogram Transformer (AST) and Whisper, and (2) models that process raw waveform inputs, including UniSpeech-SAT and HuBERT. Our experiments on the SingFake dataset evaluate these models under two input conditions—separated vocal tracks and full song mixtures—across different test subsets. The results indicate that spectrogram-based models generally outperform waveform-based models, notably on unseen singers. Metrics such as Precision, Recall, F1-score, Equal Error Rate (EER), and Area Under the Curve (AUC) provide insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. Our findings contribute to developing more effective deepfake singing detection methods, with implications for security, media authentication, and digital content protection. © 2013 IEEE.
- IEEE AccessCapturing Semantic Relationships Using Full Dependency Forests to Improve Consistency in Long Document SummarizationYanjun Wu , Luong Vuong Nguyen , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2025
There are complex discourse relationships between sentences, which can be viewed as a tree structure. This semantic structure provides important information for summarization and helps to generate concise and coherent summaries. However, current neural network-based models usually treat articles as simple sentence sequences, ignoring the intrinsic structure. To integrate discourse tree information, we propose a generative summarization model that incorporates tree structure. The article’s structure can be more accurately captured by this model, which can also produce succinct summaries by leveraging the semantic dependencies of the source material. Also, since large models are difficult to apply in downstream tasks, we try to add noise to the pre-training parameters to improve the performance of the model on the long document summarization task. Experimental results show that our model ROUGE scores outperform the state-of-the-art best models in both pubMed and arXiv datasets. We further performed human evaluation, and N-gram evaluation. The results show that our method also improves the cohesiveness and semantic coherence of abstracts. © 2013 IEEE.
- IEEE AccessTransmission Power Optimization for Hybrid NOMA-URLLC System With STAR-RIS AssistanceTra Huong Thi Le , Nguyen Van Dien , Luong Vuong Nguyen , Tri-Hai Nguyen , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2025
The simultaneous transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) has recently emerged as a cutting-edge technology for future wireless networks. In this paper, we explore an uplink STAR-RIS-enabled ultra-reliable and low-latency communications (URLLC) system utilizing hybrid non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA). To enhance system performance, we pair one transmitting user with one reflecting user as a NOMA pair. Using a time division multiple access (TDMA) protocol among different pairs, our goal is to minimize the overall transmission power while meeting the individual reliability requirements of each user. This is achieved through joint optimization of block length and transmit power of users alongside beamforming design at the STAR-RIS. This non-convex optimization problem is then effectively approximated by estimating the channel dispersion in both the high signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) regime and across the entire practical SINR range. Then, we address this power minimization problem using an alternating optimization approach. Simulation results demonstrate the advantages of the proposed framework over conventional approaches, such as conventional RIS-based and OMA-based systems. Moreover, beamforming design, block-length optimization, and the rising of the element number of STAR-RIS significantly impact power reduction performance. © 2013 IEEE.
-
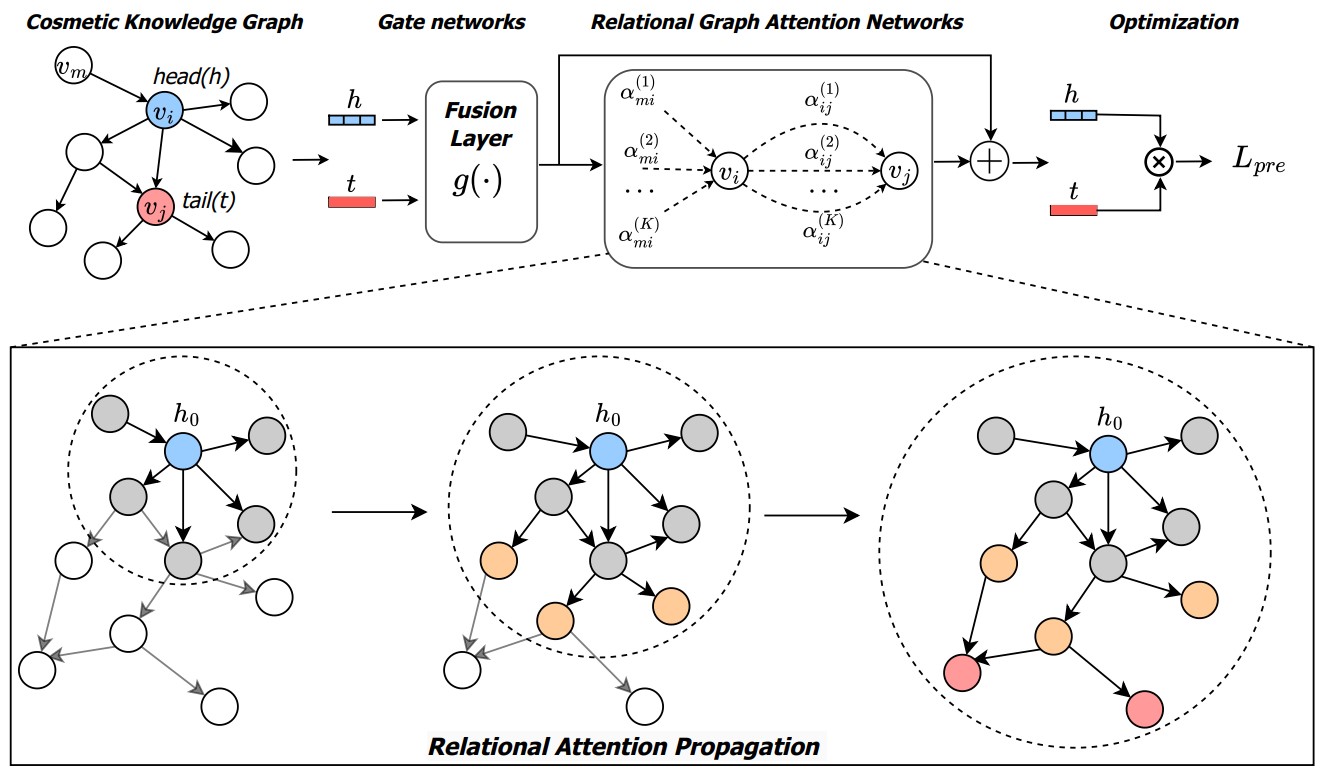 Halal or Not: Knowledge Graph Completion for Predicting Cultural Appropriateness of Daily ProductsVan Thuy Hoang, Tien-Bach-Thanh Do, Jinho Seo , Seung Charlie Kim , Luong Vuong Nguyen, Duong Nguyen Minh Huy , Hyeon-Ju Jeon , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2025
Halal or Not: Knowledge Graph Completion for Predicting Cultural Appropriateness of Daily ProductsVan Thuy Hoang, Tien-Bach-Thanh Do, Jinho Seo , Seung Charlie Kim , Luong Vuong Nguyen, Duong Nguyen Minh Huy , Hyeon-Ju Jeon , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2025The growing demand for halal cosmetic products has exposed significant challenges, especially in Muslim-majority countries. Recently, various machine learning-based strategies, e.g., image-based methods, have shown remarkable success in predicting the halal status of cosmetics. However, these methods mainly focus on analyzing the discrete and specific ingredients within separate cosmetics, which ignore the high-order and complex relations between cosmetics and ingredients. To address this problem, we propose a halal cosmetic recommendation framework, namely HaCKG, that leverages a knowledge graph of cosmetics and their ingredients to explicitly model and capture the relationships between cosmetics and their components. By representing cosmetics and ingredients as entities within the knowledge graph, HaCKG effectively learns the high-order and complex relations between entities, offering a robust method for predicting halal status. Specifically, we first construct a cosmetic knowledge graph representing the relations between various cosmetics, ingredients, and their properties. We then propose a pre-trained relational graph attention network model with residual connections to learn the structural relation between entities in the knowledge graph. The pre-trained model is then fine-tuned on downstream cosmetic data to predict halal status. Extensive experiments on the cosmetic dataset over halal prediction tasks demonstrate the superiority of our model over state-of-the-art baselines. © 2025 The Authors.
2024
- ICITMoviePoster-Grounded Contextual Visualization Using Multimodal TechniquesHuu-Tuong Ho , Minh-Tien Pham , Quang-Duong Tran , Quang-Huy Pham , Quang Dieu Tran , Ngoc Phi Nguyen , O-Joun Lee, and Luong Vuong NguyenIn Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Intelligence of Things (ICIT 2024) , 2024
This study introduces an innovative approach to contextual visualization in movies called MoviePoster-Grounded Contextual Visualization (MPCV). Leveraging multimodal techniques, MPCV integrates textual and visual information, primarily focusing on movie posters, to enhance the exploration of movie-related datasets. By combining these modalities, MPCV seeks to reveal latent patterns and connections within movie datasets, offering a more comprehensive and contextually enriched visualization experience. To validate the effectiveness of MPCV, we conduct a thorough review of related work in movie poster analysis, genre classification, and recommendation systems. In particular, we have salvaged the advantages of pre-trained models such as MobileNetV3, Inception-v3, EfficientNetV2, and BLIP-2 to present a descriptive movie poster visualization. © The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2024.
- ICCE-AsiaAn Overview of Pre-Trained Graph Models for Molecular Structure AnalysisVan Thuy Hoang , and O-Joun LeeIn Proceedings of the 9th IEEE/IEIE International Conference On Consumer Electronics Asia (ICCE-Asia 2024) , 2024
Molecules are naturally represented as graphs, which benefit graph models in understanding molecular structures to capture complex relationships and interactions between atoms. However, the limitations of labeled molecules can significantly impact the graph model’s ability to generalize different molecular properties and structures, leading to poor performance. Lately, pretraining Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a powerful tool for learning molecular representations, addressing the challenge due to the lack of labeled molec-ular data. This study introduces and examines the pretraining GNNs strategies in learning molecular structure in computational chemistry and biology. We first categorize recent pretraining existing studies into three main groups: node-level strategies, contrastive learning, and graph-level strategies. Furthermore, we also highlight recent studies that significantly enhance model interpretability and prediction accuracy. This comprehensive perspective on the current state and future prospects of GNNs underscores their pivotal role in accelerating drug discovery and material innovation through advanced AI-driven analysis. © 2024 IEEE.
- IEEE AccessFace Detection Using Eigenfaces: A Comprehensive ReviewHuu-Tuong Ho , Luong Vuong Nguyen, Tra Le Thi Huong , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2024
This paper thoroughly reviews face detection techniques, primarily focusing on applying Eigenfaces, a powerful method rooted in Principal Component Analysis (PCA). The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the advancements, challenges, and prospects associated with Eigenface-based face detection systems. The review commences with exploring the comprehensive facial recognition system framework using Eigenfaces and studying the intricacies of employing Eigenfaces as a foundational element for robust facial recognition. Then, we describe the taxonomies of various Eigenface-based face detection approaches to provide a systematic understanding of the diverse strategies utilized in Eigenface-based face detection systems. Besides, the paper explores benchmarking datasets tailored specifically for facial recognition. These datasets are critically analyzed, highlighting their relevance, limitations, and potential impact on developing and assessing Eigenface-based face detection algorithms. Furthermore, the review details the limitations and open issues inherent in Eigenface-based face detection systems. Addressing concerns such as sensitivity to lighting conditions, occlusions, and scalability, this section aims to guide future research directions by identifying gaps in the current understanding and proposing potential avenues for improvement. © 2013 IEEE.
- J Mater Chem CA neural compact model based on transfer learning for organic FETs with Gaussian disorderMinsun Cho , Marin Franot , O-Joun Lee , and Sungyeop JungJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 2024
We present an approach to adopt deep neural networks for the development of a compact model for transistors, namely a neural compact model, including transfer learning to enhance accuracy and reduce model development time. We examine the effectiveness of this approach when the electrical data for neural networks is scarce and costly and when the electrical characteristics to be modeled are highly non-linear. By using technology computer-aided design simulations, we constructed a dataset of the electrical characteristics of organic field-effect transistors with Gaussian disorder that exhibit highly non-linear current-voltage curves. Subsequently, we developed neural compact models by modifying conventional deep learning models and validated the effectiveness of transfer learning with testing through various experiments. We showed that the neural compact model with transfer learning provides an equivalent accuracy at a significantly shorter training time. © 2024 The Royal Society of Chemistry.
- npj Clean WaterInternal pipe corrosion assessment method in water distribution system using ultrasound and convolutional neural networksYeongho Sung , Hyeon-Ju Jeon, Daehun Kim , Min-Seo Kim , Jaeyeop Choi , Hwan Ryul Jo , Junghwan Oh , O-Joun Lee, and Hae Gyun Limnpj Clean Water, 2024
Internal pipe corrosion within water distribution systems leads to iron oxide deposits on pipe walls, potentially contaminating the water supply. Consuming iron oxide-contaminated water can cause significant health issues such as gastrointestinal infections, dermatological problems, and lymph node complications. Therefore, non-destructive and continuous monitoring of pipe corrosion is imperative for water sustainability initiatives. This study introduces a dual-mode methodology utilizing advanced ultrasound technology and convolutional neural networks (CNN) to quantify pipe corrosion. Scanning acoustic microscopy (SAM) employs high-frequency ultrasound to generate high-resolution images of pipe thickness, indicating iron oxide accumulation. SAM also captures internal pipe data to measure iron oxide concentration in the water. This data, analyzed by CNN, achieves an impressive 95% accuracy. This dual-mode system effectively assesses both the extent of pipe corrosion and water contamination, exemplifying the successful integration of SAM and CNN for precise and reliable monitoring. © The Author(s) 2024.
-
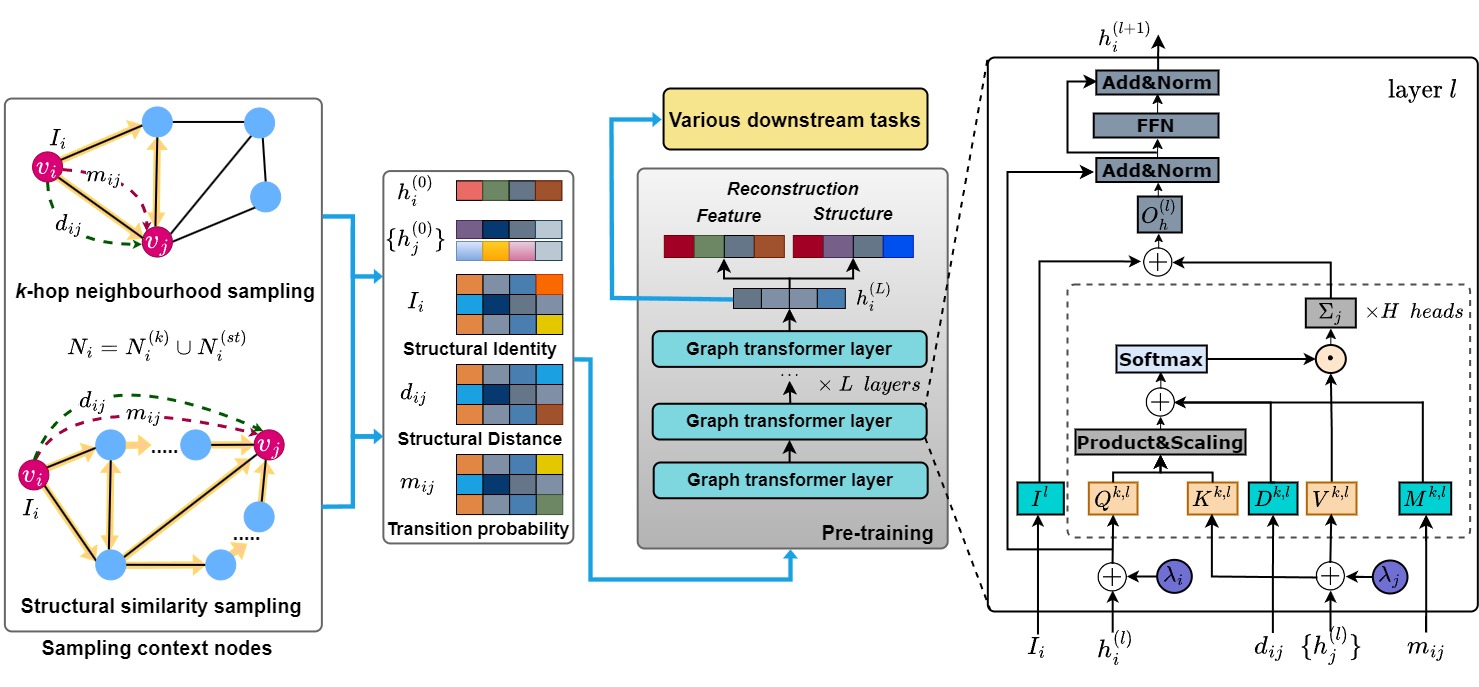 Transitivity-Preserving Graph Representation Learning for Bridging Local Connectivity and Role-Based SimilarityVan Thuy Hoang , and O-Joun LeeIn Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024) , 2024
Transitivity-Preserving Graph Representation Learning for Bridging Local Connectivity and Role-Based SimilarityVan Thuy Hoang , and O-Joun LeeIn Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024) , 2024Graph representation learning (GRL) methods, such as graph neural networks and graph transformer models, have been successfully used to analyze graph-structured data, mainly focusing on node classification and link prediction tasks. However, the existing studies mostly only consider local connectivity while ignoring long-range connectivity and the roles of nodes. In this paper, we propose Unified Graph Transformer Networks (UGT) that effectively integrate local and global structural information into fixed-length vector representations. First, UGT learns local structure by identifying the local substructures and aggregating features of the k-hop neighborhoods of each node. Second, we construct virtual edges, bridging distant nodes with structural similarity to capture the long-range dependencies. Third, UGT learns unified representations through self-attention, encoding structural distance and p-step transition probability between node pairs. Furthermore, we propose a self-supervised learning task that effectively learns transition probability to fuse local and global structural features, which could then be transferred to other downstream tasks. Experimental results on real-world benchmark datasets over various downstream tasks showed that UGT significantly outperformed baselines that consist of state-of-the-art models. In addition, UGT reaches the third-order Weisfeiler-Lehman power to distinguish non-isomorphic graph pairs. Copyright © 2024, Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved.
-
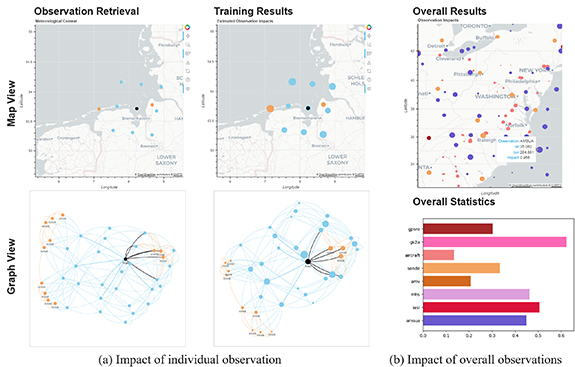 Observation impact explanation in atmospheric state estimation using hierarchical message-passing graph neural networksHyeon-Ju Jeon, Jeon-Ho Kang , In-Hyuk Kwon , and O-Joun LeeMachine Learning: Science and Technology, 2024
Observation impact explanation in atmospheric state estimation using hierarchical message-passing graph neural networksHyeon-Ju Jeon, Jeon-Ho Kang , In-Hyuk Kwon , and O-Joun LeeMachine Learning: Science and Technology, 2024The impact of meteorological observations on weather forecasting varies with the sensor type, location, time, and other environmental factors. Thus, the quantitative analysis of observation impacts is crucial for the effective and efficient development of weather forecasting systems. However, existing impact analysis methods are dependent on specific forecast systems, because system-specific adjoint models are used and the sensitivity of the observation to the forecast is measured. This study investigates the impact of observations on atmospheric state estimation in weather forecasting systems by developing a novel graph neural network (GNN) model specialized for analyzing the heterogeneous relations between observations and atmospheric states. The observation impact can then be assessed by applying explainable methods to the proposed GNN model, which is independent of forecasting systems. Further, we develop a novel application called ‘CloudNine,’ a system that provides impact analysis for individual observations with visualization. Our GNN model comprises hierarchical message-passing modules that separately analyze spatial correlations between observations at close locations and atmospheric states at close locations and then examine correlations between observations and atmospheric states. To consider the different factors influencing these correlations, we utilized geo-coordinates and types of observations in the attention mechanism of the modules with their feature vectors. We then applied gradient-based explainability methods to quantify the significance of the different observations in the estimation. Evaluated using data from 11 satellites and land-based observations, the results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed model and the visualization of observation impacts, enhancing the understanding and optimization of observational data in weather forecasting. © 2024 The Author(s). Published by IOP Publishing Ltd.
-
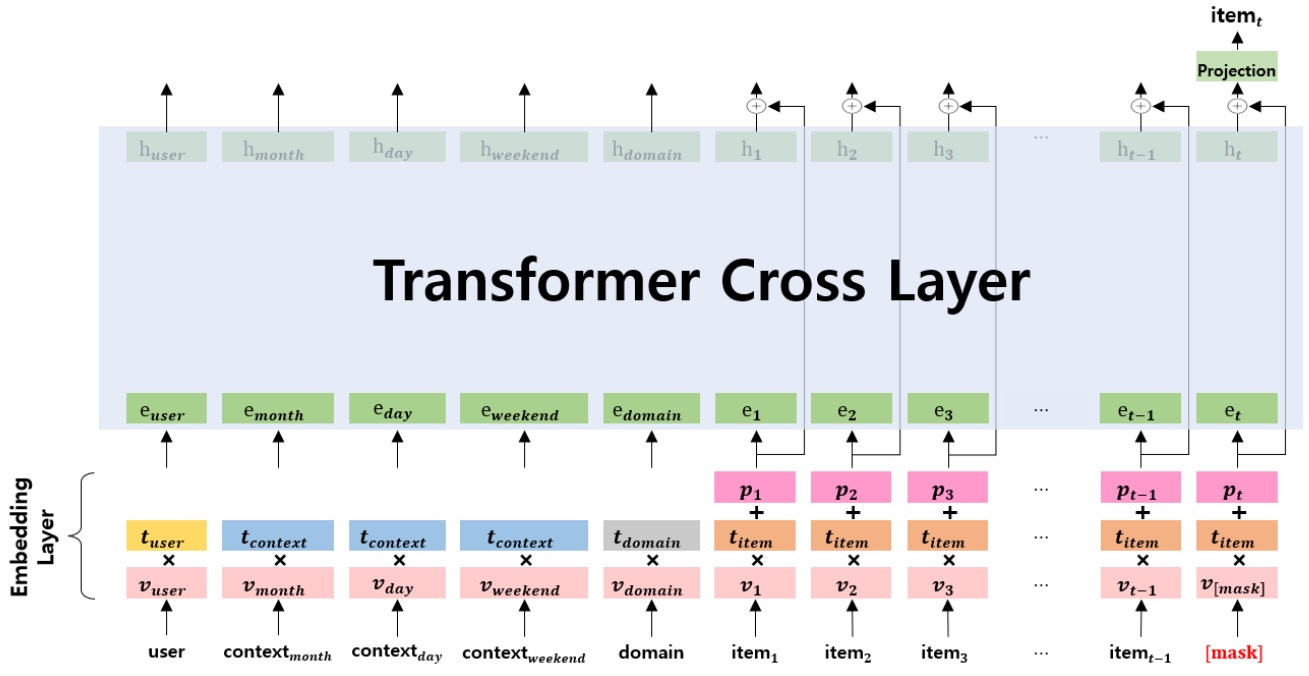 Kiosk Recommend System Based On Self-Supervised Representation Learning of User Behaviors in Offline RetailIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024
Kiosk Recommend System Based On Self-Supervised Representation Learning of User Behaviors in Offline RetailIEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024Recently, in the offline distribution field, as the number of data collection and analysis cases increases by applying IoT devices to kiosks, research on hyper-personalized recommendation systems has become critical. Recommendation systems only work well in some data-rich areas (industries). Therefore, it is unsuitable for kiosk systems with multiple domains and data imbalances, and it is challenging to collect detailed information such as user reviews and product descriptions. In this paper, we propose a context-aware hyper-personalized recommendation system that utilizes context information collected from kiosk IoT devices, minimizes the model size of the kiosk device, and aims for consistent performance and high recommendation performance in various domains. We also developed effective self-supervised learning to increase data learning efficiency in data imbalance environments. The quality of products recommended by the proposed kiosk recommendation system was evaluated using transactions that occurred in an actual kiosk system. As a result, compared to the existing recommendation system, all performance indicators improved by an average of 20%. When the self-supervised learning method was additionally applied, it improved by an average of 0.8% more. In particular, it shows superior performance regarding the quality of recommended items and resource usage according to users. IEEE
- IEEE Sens JQuantification of dysnatremia using single-beam acoustic microbeam and convolutional neural networksJi Won Nam , Hyeon-Ju Jeon , Jeong Eun Lee , O-Joun Lee, and Hae Gyun LimIEEE Sensors Journal, 2024
Recently, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in cell analysis has gained significant attention, with particular focus on ultrasound-based AI for single-cell analysis. One application is diagnosing diseases by using ultrasound signals to analyze the physical properties contained in the signals. Dysnatremia, which can result in severe consequences to health such as stroke and cardiovascular disease, can be measured using blood sodium tests. However, these tests are performed by drawing blood, and obtaining the results requires a considerable amount of time. In addition, it has low reliability because the results vary depending on the inspection equipment and inspection method. In this study, we propose a novel approach for the quantification of dysnatremia using a single-beam acoustic microbeam (SBAM) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). A 90 MHz transducer was fabricated and used to obtain reflected signals from red blood cells (RBCs), which are affected by the shape of the cells which, in turn, depend on the sodium concentration. Blood samples with varying sodium chloride concentrations were tested, and the reflected signals were analyzed using a CNN, for automation as opposed to manual analysis. The accuracy of the classification of the blood samples into 10 and 5-level groups, based on the sodium chloride concentration, was 0.961 and 0.942, respectively, as determined using CNNs. The results of this study demonstrate the potential of SBAM and CNN technologies for efficient quantification of sodium concentration in blood. This technology will help to diagnose dysnatremia in a non-invasive way with reduced analysis time and high accuracy. IEEE
- UltrasonicsDiagnosis of diabetes mellitus using high frequency ultrasound and convolutional neural networkJeong Eun Lee , Hyeon-Ju Jeon , O-Joun Lee, and Hae Gyun LimUltrasonics, 2024
The incidence of diabetes mellitus has been increasing, prompting the search for non-invasive diagnostic methods. Although current methods exist, these have certain limitations, such as low reliability and accuracy, difficulty in individual patient adjustment, and discomfort during use. This paper presents a novel approach for diagnosing diabetes using high-frequency ultrasound (HFU) and a convolutional neural network (CNN). This method is based on the observation that glucose in red blood cells (RBCs) forms glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and accumulates on its surface. The study incubated RBCs with different glucose concentrations, collected acoustic reflection signals from them using a custom-designed 90-MHz transducer, and analyzed the signals using a CNN. The CNN was applied to the frequency spectra and spectrograms of the signal to identify correlations between changes in RBC properties owing to glucose concentration and signal features. The results confirmed the efficacy of the CNN-based approach with a classification accuracy of 0.98. This non-invasive diagnostic technology using HFU and CNN holds promise for in vivo diagnosis without the need for blood collection. © 2023
- BMC Med ImgAutomated classification of liver fibrosis stages using ultrasound imagingHyun-Cheol Park , YunSang Joo , O-Joun Lee , Kunkyu Lee , Tai-Kyong Song , Chang Choi , Moon Hyung Choi , and Changhan YoonBMC Medical Imaging, 2024
Background: Ultrasound imaging is the most frequently performed for the patients with chronic hepatitis or liver cirrhosis. However, ultrasound imaging is highly operator dependent and interpretation of ultrasound images is subjective, thus well-trained radiologist is required for evaluation. Automated classification of liver fibrosis could alleviate the shortage of skilled radiologist especially in low-to-middle income countries. The purposed of this study is to evaluate deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) for classifying the degree of liver fibrosis according to the METAVIR score using US images. Methods: We used ultrasound (US) images from two tertiary university hospitals. A total of 7920 US images from 933 patients were used for training/validation of DCNNs. All patient were underwent liver biopsy or hepatectomy, and liver fibrosis was categorized based on pathology results using the METAVIR score. Five well-established DCNNs (VGGNet, ResNet, DenseNet, EfficientNet and ViT) was implemented to predict the METAVIR score. The performance of DCNNs for five-level (F0/F1/F2/F3/F4) classification was evaluated through area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) with 95% confidential interval, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratio. Results: Similar mean AUC values were achieved for five models; VGGNet (0.96), ResNet (0.96), DenseNet (0.95), EfficientNet (0.96), and ViT (0.95). The same mean accuracy (0.94) and specificity values (0.96) were yielded for all models. In terms of sensitivity, EffcientNet achieved highest mean value (0.85) while the other models produced slightly lower values range from 0.82 to 0.84. Conclusion: In this study, we demonstrated that DCNNs can classify the staging of liver fibrosis according to METAVIR score with high performance using conventional B-mode images. Among them, EfficientNET that have fewer parameters and computation cost produced highest performance. From the results, we believe that DCNNs based classification of liver fibrosis may allow fast and accurate diagnosis of liver fibrosis without needs of additional equipment for add-on test and may be powerful tool for supporting radiologists in clinical practice. © The Author(s) 2024.
2023
- EACL“Why do I feel offended?’ Korean Dataset for Offensive Language IdentificationSan-Hee Park , Kang-Min Kim , O-Joun Lee, Youjin Kang , Jaewon Lee , Su-Min Lee , and SangKeun LeeIn Proceedings of the 17th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (EACL 2023) , 2023
Offensive content is an unavoidable issue on social media. Most existing offensive language identification methods rely on the compilation of labeled datasets. However, existing methods rarely consider low-resource languages that have relatively less data available for training (e.g., Korean). To address these issues, we construct a novel KOrean Dataset for Offensive Language Identification (KODOLI). KODOLI comprises more fine-grained offensiveness categories (i.e., not offensive, likely offensive, and offensive) than existing ones. A likely offensive language refers to texts with implicit offensiveness or abusive language without offensive intentions. In addition, we propose two auxiliary tasks to help identify offensive languages: abusive language detection and sentiment analysis. We provide experimental results for baselines on KODOLI and observe that pre-trained language models suffer from identifying "LIKELY" offensive statements. Quantitative results and qualitative analysis demonstrate that jointly learning offensive language, abusive language and sentiment information improves the performance of offensive language identification. © 2023 Association for Computational Linguistics.
- SensorsGraph Representation Learning and Its Applications: A SurveySensors, 2023
Graphs are data structures that effectively represent relational data in the real world. Graph representation learning is a significant task since it could facilitate various downstream tasks, such as node classification, link prediction, etc. Graph representation learning aims to map graph entities to low-dimensional vectors while preserving graph structure and entity relationships. Over the decades, many models have been proposed for graph representation learning. This paper aims to show a comprehensive picture of graph representation learning models, including traditional and state-of-the-art models on various graphs in different geometric spaces. First, we begin with five types of graph embedding models: graph kernels, matrix factorization models, shallow models, deep-learning models, and non-Euclidean models. In addition, we also discuss graph transformer models and Gaussian embedding models. Second, we present practical applications of graph embedding models, from constructing graphs for specific domains to applying models to solve tasks. Finally, we discuss challenges for existing models and future research directions in detail. As a result, this paper provides a structured overview of the diversity of graph embedding models. © 2023 by the authors.
-
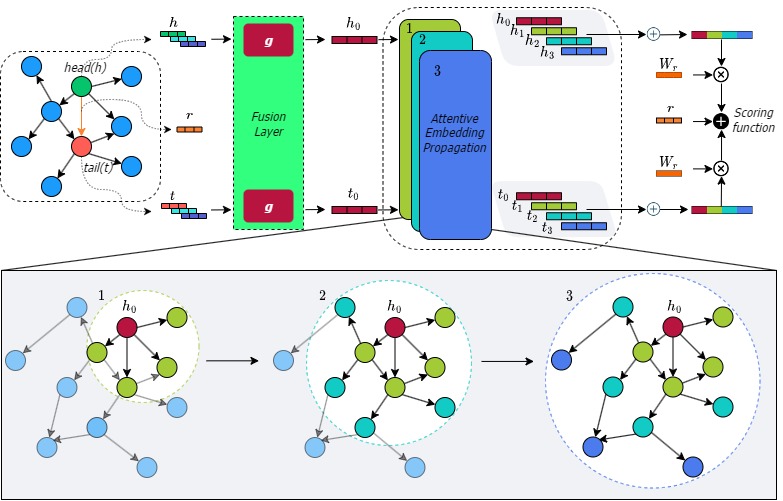 Companion Animal Disease Diagnostics Based on Literal-Aware Medical Knowledge Graph Representation LearningVan Thuy Hoang , Thanh Sang Nguyen , Sangmyeong Lee , Jooho Lee , Luong Vuong Nguyen , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2023
Companion Animal Disease Diagnostics Based on Literal-Aware Medical Knowledge Graph Representation LearningVan Thuy Hoang , Thanh Sang Nguyen , Sangmyeong Lee , Jooho Lee , Luong Vuong Nguyen , and O-Joun LeeIEEE Access, 2023Knowledge graph (KG) embedding has been used to benefit the diagnosis of animal diseases by analyzing electronic medical records (EMRs), such as notes and veterinary records. However, learning representations to capture entities and relations with literal information in KGs is challenging as the KGs show heterogeneous properties and various types of literal information. Meanwhile, the existing methods mostly aim to preserve graph structures surrounding target nodes without considering different types of literals, which could also carry significant information. In this paper, we propose a knowledge graph embedding model for the efficient diagnosis of animal diseases, which could learn various types of literal information and graph structure and fuse them into unified representations, namely LiteralKG. Specifically, we construct a knowledge graph that is built from EMRs along with literal information collected from various animal hospitals. We then fuse different types of entities and node feature information into unified vector representations through gate networks. Finally, we propose a self-supervised learning task to learn graph structure in pretext tasks and then towards various downstream tasks. Experimental results on link prediction tasks demonstrate that our model outperforms the baselines that consist of state-of-the-art models. © 2023 The Authors.
- RACSLong Short-Term Memory Network (LSTM) based Stock Price PredictionAkshat Gaurav , Varsha Arya , Kwok Tai Chui , Brij B. Gupta , Chang Choi , and O-Joun LeeIn Proceedings of the 2023 ACM International Conference on Research in Adaptive and Convergent Systems (RACS 2023) , 2023
Predicting stock prices is a challenging and highly sought-after task in financial markets. In recent years, deep learning techniques, particularly Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, have shown promising results in capturing complex temporal dependencies and forecasting time series data. This research paper presents a LSTM-based framework for stock price prediction. The proposed framework utilizes historical stock price data. The LSTM model is designed to learn the underlying patterns and trends in the data, enabling it to make accurate predictions of future stock prices. We preprocess the data, including normalization and feature engineering, to enhance the model’s ability to extract meaningful patterns. We employ appropriate evaluation metrics, such as mean squared error (MSE) and root mean squared error (RMSE), to assess the accuracy of the predictions. Experimental results demonstrate that the LSTM-based framework achieves competitive performance in stock price prediction compared to traditional statistical models and other machine learning approaches. © 2023 ACM.
- IEEE AccessClassification of Liver Fibrosis From Heterogeneous Ultrasound ImageYunsang Joo , Hyun-Cheol Park , O-Joun Lee, Changhan Yoon , Moon Hyung Choi , and Chang ChoiIEEE Access, 2023
With the advances in deep learning, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), automated diagnosis technology using medical images has received considerable attention in medical science. In particular, in the field of ultrasound imaging, CNN trains the features of organs through an amount of image data, so that an expert-level automatic diagnosis is possible only with images of actual patients. However, CNN models are also trained on the features that reflect the inherent bias of the imaging machine used for image acquisition. In other words, when the domain of data used for training is different from that of data applied for an actual diagnosis, it is unclear whether consistent performance can be provided by the domain bias. Therefore, we investigate the effect of domain bias on the model with liver ultrasound imaging data obtained from multiple domains. We have constructed a dataset considering the manufacturer and the year of manufacturing of 8 ultrasound imaging machines. First, training and testing were performed by dividing the entire data, in a commonly used method. Second, we have utilized the training data constructed according to the number of domains for the machine learning process. Then we have measured and compared the performance on internal and external domain data. Through the above experiment, we have analyzed the effect of domains of data on model performance. We show that the performance scores evaluated with the internal domain data and the external domain data do not match. We especially show that the performance measured in the evaluation data including the internal domain was much higher than the performance measured in the evaluation data consisting of the external domain. We also show that 3-level classification performance is slightly improved over 5-level classification by mitigating class imbalance by integrating similar classes. The results highlight the need to develop a new methodology for mitigating the machine bias problem so that the model can work correctly even on external domain data, as opposed to the usual approach of constructing evaluation data in the same domain as the training data. © 2013 IEEE.
2022
- SciRepAutomated estimation of cancer cell deformability with machine learning and acoustic trappingO-Joun Lee, Hae Gyun Lim, K. Kirk Shung , Jin-Taek Kim , and Hyung Ham KimScientific Reports, 2022
Cell deformability is a useful feature for diagnosing various diseases (e.g., the invasiveness of cancer cells). Existing methods commonly inflict pressure on cells and observe changes in cell areas, diameters, or thickness according to the degree of pressure. Then, the Young’s moduli (i.e., a measure of deformability) of cells are estimated based on the assumption that the degrees of the changes are inversely proportional to Young’s moduli. However, manual measurements of the physical changes in cells are labor-intensive, and the subjectivity of the operators can intervene during this step, thereby causing considerable uncertainty. Further, because the shapes of cells are nonuniform, we cannot ensure the assumption for linear correlations of physical changes in cells with their deformability. Therefore, this study aims at measuring non-linear elastic moduli of live cells (degrees of cell deformability) automatically by employing conventional neural networks (CNN) and multilayer perceptrons (MLP) while preserving (or enhancing) the accuracy of the manual methods. First, we obtain photomicrographs of cells on multiple pressure levels using single-beam acoustic tweezers, and then, we suggest an image preprocessing method for emphasizing changes in cell areas on the photomicrographs. The CNN model is trained to measure the ratios of the cell area change at each pressure level. Then, we apply the multilayer perceptron (MLP) to learn the correlations of the cell area change ratios according to the pressure levels with cell deformability. The accuracy of the CNN was evaluated using two types of breast cancer cells: MDA-MB-231 (invasive) and MCF-7 (noninvasive). The MLP was assessed using five different beads (Young’s moduli from 0.214 to 9.235 kPa), which provides standardized reference data of the non-linear elastic moduli of live cells. Finally, we validated the practicality of the proposed system by examining whether the non-linear elastic moduli estimated by the proposed system can distinguish invasive breast cancer cells from noninvasive ones. © 2022, The Author(s).
- SensorsDay-Ahead Hourly Solar Irradiance Forecasting Based on Multi-Attributed Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional NetworkHyeon-Ju Jeon , Min-Woo Choi , and O-Joun LeeSensors, 2022
Solar irradiance forecasting is fundamental and essential for commercializing solar energy generation by overcoming output variability. Accurate forecasting depends on historical solar irradiance data, correlations between various meteorological variables (e.g., wind speed, humidity, and cloudiness), and influences between the weather contexts of spatially adjacent regions. However, existing studies have been limited to spatiotemporal analysis of a few variables, which have clear correlations with solar irradiance (e.g., sunshine duration), and do not attempt to establish atmospheric contextual information from a variety of meteorological variables. Therefore, this study proposes a novel solar irradiance forecasting model that represents atmospheric parameters observed from multiple stations as an attributed dynamic network and analyzes temporal changes in the network by extending existing spatio-temporal graph convolutional network (ST-GCN) models. By comparing the proposed model with existing models, we also investigated the contributions of (i) the spatial adjacency of the stations, (ii) temporal changes in the meteorological variables, and (iii) the variety of variables to the forecasting performance. We evaluated the performance of the proposed and existing models by predicting the hourly solar irradiance at observation stations in the Korean Peninsula. The experimental results showed that the three features are synergistic and have correlations that are difficult to establish using single-aspect analysis. © 2022 by the authors.
- SciRepAutomated cell-type classification combining dilated convolutional neural networks with label-free acoustic sensingHyeon-Ju Jeon, Hae Gyun Lim, K. Kirk Shung , O-Joun Lee, and Min Gon KimScientific Reports, 2022
This study aimed to automatically classify live cells based on their cell type by analyzing the patterns of backscattered signals of cells with minimal effect on normal cell physiology and activity. Our previous studies have demonstrated that label-free acoustic sensing using high-frequency ultrasound at a high pulse repetition frequency (PRF) can capture and analyze a single object from a heterogeneous sample. However, eliminating possible errors in the manual setting and time-consuming processes when postprocessing integrated backscattering (IB) coefficients of backscattered signals is crucial. In this study, an automated cell-type classification system that combines a label-free acoustic sensing technique with deep learning-empowered artificial intelligence models is proposed. We applied an one-dimensional (1D) convolutional autoencoder to denoise the signals and conducted data augmentation based on Gaussian noise injection to enhance the robustness of the proposed classification system to noise. Subsequently, denoised backscattered signals were classified into specific cell types using convolutional neural network (CNN) models for three types of signal data representations, including 1D CNN models for waveform and frequency spectrum analysis and two-dimensional (2D) CNN models for spectrogram analysis. We evaluated the proposed system by classifying two types of cells (e.g., RBC and PNT1A) and two types of polystyrene microspheres by analyzing their backscattered signal patterns. We attempted to discover cell physical properties reflected on backscattered signals by controlling experimental variables, such as diameter and structure material. We further evaluated the effectiveness of the neural network models and efficacy of data representations by comparing their accuracy with that of baseline methods. Therefore, the proposed system can be used to classify reliably and precisely several cell types with different intrinsic physical properties for personalized cancer medicine development. © 2022, The Author(s).
2021
- Comp4HumanComputing4Human 2021: The 2nd international conference on human-centered artificial intelligenceNam D. Vo , O-Joun Lee, Khac-Hoai Nam Bui , Hae Gyun Lim, Hyeon-Ju Jeon , Phuong-Mai Nguyen , Jin-Taek Kim , Bui Quang Tuyen , Jason J. Jung, and Thuy Anh VoIn Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Human-centered Artificial Intelligence (Computing4Human 2021) , 2021
The 2nd international conference on human-centered artificial intelligence (Computing4Human) is hosted by the University of Economics, The University of Danang, on the 28th of October 2021. This conference tackled various research areas: the Computational Humanities and Social Sciences, Smart Infrastructure, Smart Healthcare, Secure and Green IoT Communications, Explainable Recommendation and Retrieval, and Business Intelligence. We collected 35 papers, which were fully refereed and underwent a single-blind review process by at least three reviewers. Finally, 26 papers have been published for six technical tracks. © 2021 CEUR-WS. All rights reserved.
- MISInterinstitutional Research Team Formation Based on Bibliographic Network EmbeddingO-Joun Lee, Seungha Hong , and Jin-Taek KimMobile Information Systems, 2021
This study aims at forming research teams for interinstitutional collaborations. Research institutes have their own purposes and topics of interest. Thus, supporting joint research between multiple institutes, we have to consider not only synergies between scholars but also purposes of the institutes. To solve this problem, we propose a bibliographic network embedding method that can learn characteristics of institutes, not only of each scholar. First, we compose a bibliographic network that consists of scholars, publications, venues, research projects, and institutes. Collaboration styles and research topics of institutes and scholars are extracted by mining subgraphs from the bibliographic network. Then, vector representations of network nodes are learned based on occurrences of subgraphs on the nodes and neighborhoods of the nodes. Based on the vector representations, we train multilayer perceptrons (MLP) to assess collaboration probability between scholars affiliated in different institutes. For training the MLP, we suggest three strategies: (i) considering every collaboration, (ii) focusing on interinstitutional collaborations, and (iii) focusing on collaboration outcomes. To evaluate the proposed methods, we have analyzed research collaborations of POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) and RIST (Research Institute of Industrial Science and Technology) from 2011 to 2020. Then, we conducted the research team formation for joint research of the two institutes according to two purposes: pure research and commercialization research. © 2021 O-Joun Lee et al.
-
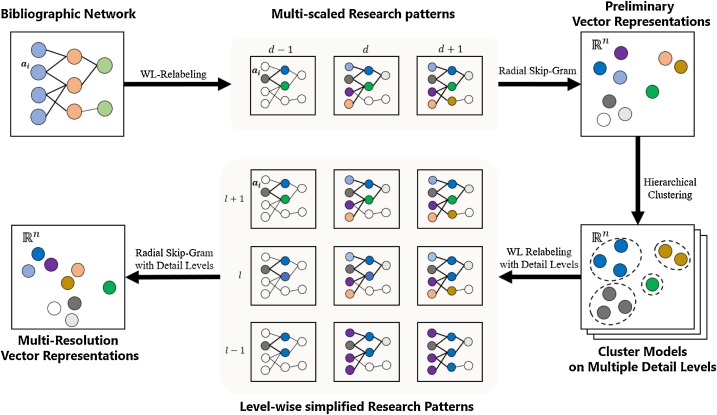 Learning multi-resolution representations of research patterns in bibliographic networksO-Joun Lee, Hyeon-Ju Jeon, and Jason J. JungJournal of Informetrics, 2021
Learning multi-resolution representations of research patterns in bibliographic networksO-Joun Lee, Hyeon-Ju Jeon, and Jason J. JungJournal of Informetrics, 2021This study aims at representing research patterns of bibliographic entities (e.g., scholars, papers, and venues) with a fixed-length vector. Bibliographic network structures rooted in the entities are incredibly diverse, and this diversity increases in the outstanding entities. Thus, despite their significant volume, the outstanding entities obtain minimal learning opportunities, whereas low-performance entities are over-represented. This study solves the problem by representing the patterns of the entities rather than depicting individual entities in a precise manner. First, we describe structures rooted in the entities using the Weisfeiler-Lehman (WL) relabeling process. Each subgraph generated by the relabeling process provides information on the scholars, kinds of papers they published, standards of venues in which the papers were published, and types of their collaborators. We assume that a subgraph depicts the research patterns of bibliographic entities, such as the preference of a scholar in choosing either a few highly impactful papers or numerous papers of moderate impact. Then, we simplify the subgraphs according to multiple levels of detailedness. Original subgraphs represent the individuality of the entities, and simplified subgraphs represent the entities sharing the same research patterns. In addition, simplified subgraphs balance the learning opportunities of high- and low-performance entities by co-occurring with both types of entities. We embed the subgraphs using the Skip-Gram method. If the results of the embedding represent the research patterns of the entities, the obtained vectors should be able to represent various aspects of the research performance in both the short-term and long-term durations regardless of the performances of the entities. Therefore, we conducted experiments for predicting 23 performance indicators during four time periods for four performance groups (top 1%, 5%, 10%, and all entities) using only the vector representations. The proposed model outperformed the existing network embedding methods in terms of both accuracy and variance. © 2020 Elsevier Ltd.
- AppSciPlot structure decomposition in narrative multimedia by analyzing personalities of fictional charactersO-Joun Lee, Eun-Soon You, and Jin-Taek KimApplied Sciences (Switzerland), 2021
This study aims to decompose plot structures of stories in narrative multimedia (i.e., creative works that contain stories and are distributed through multimedia). Since a story is interwoven with main plots and subplots (i.e., primary and ancillary story lines), decomposing a story into multiple story lines enables us to analyze how events in the story are allocated and logically connected. For the decomposition, the existing studies employed character networks (i.e., social networks of characters that appeared in a story) and assumed that characters’ social relationships are consistent in a story line. However, these studies overlooked that social relationships significantly change around major events. To solve this problem, we attempt to use the changes for distinguishing story lines rather than suffer from the changes. We concentrate on the changes in characters’ social relationships being the result of changes in their personalities. Moreover, these changes gradually proceed within a story line. Therefore, we first propose features for measuring changes in personalities of characters: (i) Degrees of characters in character networks, (ii) lengths of dialogues spoken by characters, and (iii) ratios of out-degrees for in-degrees of characters in character networks. We supposed these features reflect importance, inner/outer conflicts, and activeness of characters, respectively. Since characters’ personalities gradually change in a story line, we can suppose that the features also show gradual story developments in a story line. Therefore, we conduct regression for each feature to discover dominant tendencies of the features. By filtering scenes that do not follow the tendencies, we extract a story line that exhibits the most dominant personality changes. We can decompose stories into multiple story lines by iterating the regression and filtering. Besides, personalities of characters change more significantly in major story lines. Based on this assumption, we also propose methods for discriminating main plots. Finally, we evaluated the accuracy of the proposed methods by applying them to the movies, which is one of the most popular narrative multimedia. © 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
- Comp4HumanLearning contextual representations of citations via graph transformerHyeon-Ju Jeon , Gyu-Sik Choi , Se-Young Cho , Hanbin Lee , Hee Yeon Ko , Jason J. Jung , O-Joun Lee, and Myeong-Yeon YiIn Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Human-centered Artificial Intelligence (Computing4Human 2021) , 2021
This study aims at representing the citation based on the citation context extracted from the citation network. Researchers cite papers for various purposes to describe their arguments in a logical structure. Thus, citations have different roles depending on what structure they are cited in the paper. In this paper, we first present a definition of the citation context and initialize the embedding vector based on the citation order and location. Then, based on the graph transformer model, we learn contextual citation embeddings. To represent citation context, we consider the following three parts: (i) textual features of paper, (ii) positional features of the citation context, and (iii) structural features of the citation network by applying the self-attention mechanism. © 2021 CEUR-WS. All rights reserved.
- Comp4HumanQuantifying conflicts in narrative multimedia by analyzing visual storytelling techniquesO-Joun Lee, Jin-Taek Kim , and Eun-Soon YouIn Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Human-centered Artificial Intelligence (Computing4Human 2021) , 2021
This study aims at measuring conflict degrees of each shot in visual narrative multimedia (e.g., movies and TV series) by analyzing visual storytelling techniques, such as camerawork. To describe incidents in stories, directors use the techniques as like as visual language. Thus, visual storytelling techniques used in a shot should be correlated with incidents shown by the shot. In this study, we first present various taxonomies of the visual storytelling techniques and discuss which techniques have more correlations with conflicts than the others. Then, based on usages of the techniques in each shot, we measure intensity of conflicts described by the shot. Finally, we validated correlations of visual storytelling techniques with stories’ content by examining correlations of the proposed conflict measurement with conflict degrees annotated by scholars and practitioners in film studies. Copyright © by the paper’s authors. Use permitted under Creative Commons License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
2020
- IJCAIStory embedding: Learning distributed representations of stories based on character networksO-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2020) , 2020
This study aims to represent stories in narrative works (i.e., creative works that contain stories) with a fixed-length vector. We apply subgraph-based graph embedding models to dynamic social networks of characters that appeared in stories (character networks). We suppose that interactions between characters reflect the content of stories. We discretize the interactions by discovering the subgraphs and learn representations of stories by predicting occurrences of the subgraphs in corresponding character networks. We find subgraphs rooted in each character on each scene in multiple scales, using the WL (Weisfeiler-Lehman) relabeling process. To predict occurrences of subgraphs, we apply two approaches: (i) considering changes in subgraphs according to scenes and (ii) focusing on subgraphs on the last scene. We evaluated the proposed models by measuring the similarity between real movies with vector representations that were generated by the models. © 2020 Inst. Sci. inf., Univ. Defence in Belgrade. All rights reserved.
- Comp4HumanDiscovering mise-en-scène in movies by analyzing scriptsO-Joun Lee, and Jin-Taek KimIn Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Computational Humanities and Social Sciences (Computing4Human 2020) , 2020
This study aims to analyze mise-en-scène in movies. Although the mise-en-scène includes all the entities that appear on the scene, we focus on metaphorical meanings of the entities. When entities are expressions of the same metaphorical symbol, lexical meanings of the entities will be relevant to each other. Also, if a metaphorical symbol is significant for storytelling, the symbol will appear on most of the scenes. Therefore, we find groups of entities, which share similar lexical meanings and appear allover the movie. As a preliminary study, we have applied these approaches on terms in movie scripts with simple natural language processing techniques. Although we have not conducted evaluation yet, we anticipate that the proposed method will be helpful for analyzing artistic and topical intentions of movie directors. Copyright © by the paper’s authors. Use permitted under Creative Commons License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
- JAIHCA novel network virtualization based on data analytics in connected environmentKhac-Hoai Nam Bui , Sungrae Cho , Jason J. Jung, Joongheon Kim , O-Joun Lee, and Woongsoo NaJournal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2020
Big data analytics is a growing trend for network and service management. Some approaches such as statistical analysis, data mining and machine learning have become promising techniques to improve operations and management of information technology systems and networks. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach for network management in terms of abnormality detection based on data analytics. Particularly, the main research focuses on how the network configuration can be automatically and adaptively decided, given various dynamic contexts (e.g., network interference, heterogeneity and so on). Specifically, we design a context-based data-driven framework for network operation in connected environment which includes three layer architecture: (i) network entity layer; (ii) complex semantic analytics layer and (iii) action provisioning layer. A case study on interference-based abnormal detection for connected vehicle explains more detail about our work. © 2018, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
- AIJStory embedding: Learning distributed representations of stories based on character networksO-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungArtificial Intelligence, 2020
This study aims to learn representations of stories in narrative works (i.e., creative works that contain stories) using fixed-length vectors. Vector representations of stories enable us to compare narrative works regardless of their media or formats. To computationally represent stories, we focus on social networks among characters (character networks). We assume that the structural features of the character networks reflect the characteristics of stories. By extending substructure-based graph embedding models, we propose models to learn distributed representations of character networks in stories. The proposed models consist of three parts: (i) discovering substructures of character networks, (ii) embedding each substructure (Char2Vec), and (iii) learning vector representations of each character network (Story2Vec). We find substructures around each character in multiple scales based on proximity between characters. We suppose that a character’s substructures signify its ‘social roles’. Subsequently, a Char2Vec model is designed to embed a social role based on co-occurred social roles. Since character networks are dynamic social networks that temporally evolve, we use temporal changes and adjacency of social roles to determine their co-occurrence. Finally, Story2Vec models predict occurrences of social roles in each story for embedding the story. To predict the occurrences, we apply two approaches: (i) considering temporal changes in social roles as with the Char2Vec model and (ii) focusing on the final social roles of each character. We call the embedding model with the first approach ‘flow-oriented Story2Vec.’ This approach can reflect the context and flow of stories if the dynamics of character networks is well understood. Second, based on the final states of social roles, we can emphasize the denouement of stories, which is an overview of the static structure of the character networks. We name this model as ‘denouement-oriented Story2Vec.’ In addition, we suggest ‘unified Story2Vec’ as a combination of these two models. We evaluated the quality of vector representations generated by the proposed embedding models using movies in the real world. © 2020 Elsevier B.V.
- CancersClassification of breast cancer cells using the integration of high-frequency single-beam acoustic tweezers and convolutional neural networksHae Gyun Lim , O-Joun Lee, K. Kirk Shung , Jin-Taek Kim , and Hyung Ham KimCancers, 2020
Single-beam acoustic tweezers (SBAT) is a widely used trapping technique to manipulate microscopic particles or cells. Recently, the characterization of a single cancer cell using high-frequency (>30 MHz) SBAT has been reported to determine its invasiveness and metastatic potential. Investigation of cell elasticity and invasiveness is based on the deformability of cells under SBAT’s radiation forces, and in general, more physically deformed cells exhibit higher levels of invasiveness and therefore higher metastatic potential. However, previous imaging analysis to determine substantial differences in cell deformation, where the SBAT is turned ON or OFF, relies on the subjective observation that may vary and requires follow-up evaluations from experts. In this study, we propose an automatic and reliable cancer cell classification method based on SBAT and a convolutional neural network (CNN), which provides objective and accurate quantitative measurement results. We used a custom-designed 50 MHz SBAT transducer to obtain a series of images of deformed human breast cancer cells. CNN-based classification methods with data augmentation applied to collected images determined and validated the metastatic potential of cancer cells. As a result, with the selected optimizers, precision, and recall of the model were found to be greater than 0.95, which highly validates the classification performance of our integrated method. CNN-guided cancer cell deformation analysis using SBAT may be a promising alternative to current histological image analysis, and this pretrained model will significantly reduce the evaluation time for a larger population of cells. © 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
- ICEATowards Story-based Summarization of Narrative MultimediaO-Joun Lee, Jin-Taek Kim , and Eun-Soon YouIn Proceedings of the 2020 ACM International Conference on Intelligent Computing and its Emerging Applications (ICEA 2020) , 2020
This study aims at summarizing narrative works (i.e., creative works that contain stories) in the consideration of their stories and types of required summaries. Various methods for story-based summarization have been proposed as a practical application of the character network analysis (i.e., a social network among characters that appeared in a story). However, the existing methods do not consider that summaries have different requirements according to their types (e.g., trailers, highlights, and recaps). These methods consist of three parts: (i) discretizing narrative works into regular units (e.g., scenes or shots), (ii) measuring the narrative significance of each unit, and (iii) generating summaries based on the narrative significance. Most of the existing studies have proposed their unique significance measurements based on individual narrative features. Also, since these methods have not considered the diverse types of summaries, they have simply selected top-N narrative units according to the measurements. In this study, we first introduce and redefine the narrative significance measurements. Subsequently, we propose a method for summarizing a narrative work regarding the requirements of the summaries by integrating the various significance measurements. © 2020 ACM.
- Comp4HumanComputing4Human 2020: The 1st international workshop on computational humanities and social sciencesJin-Taek Kim , Jason J. Jung, Eunsoon You , and O-Joun LeeIn Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Computational Humanities and Social Sciences (Computing4Human 2020) , 2020
The 1st International Workshop on Computational Humanities and Social Sciences (Computing4Human) is hosted by Future IT Innovation Laboratory (i-Lab), Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), on the 15th of February 2020. This workshop tackled various research areas: the computational narrative analysis, the technology policies, and the human-computer interaction. Copyright © by the paper’s authors. Use permitted under Creative Commons License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
- ECIRwMeasuring narrative fluency by analyzing dynamic interaction networks in textual narrativesO-Joun Lee, and Jin-Taek KimIn Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Narrative Extraction From Texts (Text2Story 2020), co-located with the 42nd European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR 2020) , 2020
This study aims to assess the fluency of narratives in textual multimedia (e.g., news articles, academic publications, novels, etc.). We measure the narrative fluency based on whether relationships between entities in the narrative (i.e., subjects and objects of events that compose the narrative) are consistently described with adequate rapidity. The relationships are represented by a dynamic interaction network (called ’entity network’), which has entities as nodes and co-occurrences between the entities as edges. Lack of consistency makes users confused about what the textual narratives want to present. If a narrative consistently concentrates on a topic or subject, its entity network will have few entities with high node centrality. Using consistency of the high centrality entities, we assess the fluency with three criteria: (i) consistency in each paragraph, (ii) consistency in the overall narrative, and (iii) consistency between the title and body. The rapidity of narrative development has to be appropriate for expected readers of the textual narratives. Too low rapidity causes redundancy, and high rapidity hinders the under-standability of the narratives. We assume structural changes in the entity network reflect the narrative rapidity. The structural change is measured by embedding structures of the entity network. Finally, we evaluated the effectiveness of the proposed methods using the editorials of the New York Times and human evaluators. Copyright © by the paper’s authors.
- RACSLearning Multi-modal Representations of Narrative Multimedia: A Case Study of WebtoonsO-Joun Lee, and Jin-Taek KimIn Proceedings of the 2020 ACM International Conference on Research in Adaptive and Convergent Systems (RACS 2020) , 2020
This study aims to learn task-agnostic representations of narrative multimedia. The existing studies focused on only stories in the narrative multimedia without considering their physical features. We propose a method for incorporating multi-modal features of the narrative multimedia into a unified vector representation. For narrative features, we embed character networks as with the existing studies. Textual features can be represented using the LSTM (Long-Short Term Memory) autoencoder. We apply the convolutional autoencoder to visual features. The convolutional autoencoder also can be used for the spectrograms of audible features. To combine these features, we propose two methods: early fusion and late fusion. The early fusion method composes representations of features on each scene. Then, we learn representations of a narrative work by predicting time-sequential changes in the features. The late fusion method concatenates feature vectors that are trained for allover the narrative work. Finally, we apply the proposed methods on webtoons (i.e., comics that are serially published through the web). The proposed methods have been evaluated by applying the vector representations to predicting the preferences of users for the webtoons. © 2020 ACM.
- SustainDiscovering social desires and conflicts from subculture narrative multimediaO-Joun Lee, Heelim Hong , Eun-Soon You, and Jin-Taek KimSustainability, 2020
This study aims at discovering social desires and conflicts from subculture narrative multimedia. Since one of the primary purposes in the subculture consumption is vicarious satisfaction, the subculture works straightforwardly describe what their readers want to achieve and break down. The latent desires and conflicts are useful for understanding our society and realizing smart governance. To discover the social issues, we concentrate on that each subculture genre has a unique imaginary world that consists of inventive subjects. We suppose that the subjects correspond to individual social issues. For example, game fiction, one of the popular genres, describes a world like video games. Under game systems, everyone gets the same results for the same efforts, and it can be interpreted as critics for the social inequality issue. Therefore, we first extract subjects of genres and measure the membership degrees of subculture works for each genre. Using the subjects and membership degrees, we build a genealogy tree of subculture genres by tracing their evolution and differentiation. Then, we extract social issues by searching for the subjects that come from the real world, not imaginary. If a subculture work criticizes authoritarianism, it might include subjects such as government officials and bureaucrats. A combination of the social issues and genre genealogy tree will show diachronic changes in our society. We have evaluated the proposed methods by extracting social issues reflected in Korean web novels. © 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
- IJCAIwIdeaNet: Potential opportunity discovery for business innovationO-Joun Lee, Sung Youn Park , and Jin-Taek KimIn Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence for Narratives Workshop (AI4Narratives 2020) held in conjunction with the 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2020) and the 17th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (PRICAI 2020) , 2020
This paper introduces an ongoing project for mining potential business opportunities from the existing business innovation cases. Crevate (a consulting company) has collected thousands of cases from news articles and columns that are in textual narratives. We aim to transform the cases into knowledge graphs that cover what kinds of ideas (e.g., untact) are applied to which industrial areas (e.g., cafe). By using link prediction methods, we will be able to evaluate the prominence of combinations (e.g., untact cafe) between ideas and domains. This study focuses on explaining the collected cases and knowledge graphs with running examples. © 2020 by the paper’s authors. Use permitted under Creative Commons License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
- SensorsLearning hierarchical representations of stories by using multi-layered structures in narrative multimediaO-Joun Lee, Jason J. Jung, and Jin-Taek KimSensors, 2020
Narrative works (e.g., novels and movies) consist of various utterances (e.g., scenes and episodes) with multi-layered structures. However, the existing studies aimed to embed only stories in a narrative work. By covering other granularity levels, we can easily compare narrative utterances that are coarser (e.g., movie series) or finer (e.g., scenes) than a narrative work. We apply the multi-layered structures on learning hierarchical representations of the narrative utterances. To represent coarser utterances, we consider adjacency and appearance of finer utterances in the coarser ones. For the movies, we suppose a four-layered structure (character roles ∈ characters ∈ scenes ∈ movies) and propose three learning methods bridging the layers: Char2Vec, Scene2Vec, and Hierarchical Story2Vec. Char2Vec represents a character by using dynamic changes in the character’s roles. To find the character roles, we use substructures of character networks (i.e., dynamic social networks of characters). A scene describes an event. Interactions between characters in the scene are designed to describe the event. Scene2Vec learns representations of a scene from interactions between characters in the scene. A story is a series of events. Meanings of the story are affected by order of the events as well as their content. Hierarchical Story2Vec uses sequential order of scenes to represent stories. The proposed model has been evaluated by estimating the similarity between narrative utterances in real movies. © 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland.
2019
- FGCSModeling affective character network for story analyticsO-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungFuture Generation Computer Systems, 2019
Consideration of the stories included in the narrative works is important for analyzing and providing narrative works (e.g., movies, novels, and comics) to users. In this study, we analyzed the stories in a narrative work with three goals: (i) eliciting, (ii) modeling, and (iii) utilizing the stories. Based upon our previous studies regarding ‘character networks’ (i.e., social networks among characters in the stories), we elicited the stories with three methods: (i) composing affective character networks with affective relationships among the characters, (ii) measuring temporal changes in tension according to the flows of the stories, and (iii) detecting affective events which refer to dramatic changes in the tension. The affective relationships contain emotional changes of the characters on each segment of the stories. By aggregating the characters’ emotional changes, we measured the tension of each segment. We called it ‘Affective Fluctuation’ and represented it as a discrete function (Affective Fluctuation Function, AFF). The AFFs enable us to detect affective events by using gradients of them and measure similarities among the stories by comparing their shapes. Also, we proposed a computational model of the stories by annotating the affective events and characters involved in those events. Finally, we demonstrated a practical application with a recommendation method which exploited the similarities between stories. Additionally, we verified the reliabilities and efficiencies of the proposed method for narrative works in the real world. © 2018 Elsevier B.V.
- FDATAIs Performance of Scholars Correlated to Their Research Collaboration Patterns?Hyeon-Ju Jeon , O-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungFrontiers in Big Data, 2019
This study aims to validate whether the research performance of scholars correlates with how the scholars work together. Although the most straightforward approaches are centrality measurements or community detection, scholars mostly participate in multiple research groups and have different roles in each group. Thus, we concentrate on the subgraphs of co-authorship networks rooted in each scholar that cover (i) overlapping of the research groups on the scholar and (ii) roles of the scholar in the groups. This study calls the subgraphs “collaboration patterns” and applies subgraph embedding methods to discover and represent the collaboration patterns. Based on embedding the collaboration patterns, we have clustered scholars according to their collaboration styles. Then, we have examined whether scholars in each cluster have similar research performance, using the quantitative indicators. The coherence of the indicators cannot be solid proofs for validating the correlation between collaboration and performance. Nevertheless, the examination for clusters has exhibited that the collaboration patterns can reflect research styles of scholars. This information will enable us to predict the research performance more accurately since the research styles are more consistent and sustainable features of scholars than a few high-impact publications. Copyright © 2019 Jeon, Lee and Jung.
- IPMIntegrating character networks for extracting narratives from multimodal dataO-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungInformation Processing and Management, 2019
This study aims to integrate diverse data within narrative multimedia (i.e., artworks containing stories and distributed through multimedia) into a unified character network (i.e., a social network between characters that appear in the story). By combining multiple data sources (e.g., the text, video, and audio), we attempted to enhance the accuracy and semantic richness of existing character networks that confine themselves to a particular data source. To merge various data, we propose story synchronization for (i) improving the accuracy of data extracted from the narrative multimedia and (ii) integrating the data into the unified character network. The story synchronization mainly consists of three steps: synchronizing (i) scenes, (ii) characters, and (iii) character networks. First, we synchronize dialogues in the text and audio, to discover speakers and time of dialogues. This enables us to segment the scene using time periods when dialogues (in the text and audio) and characters (in the video) do not commonly occur. Through the scene segmentation, we can discretize stories in the narrative work. By comparing the occurrence of dialogues and characters in each scene, we synchronize identities of the characters in the text and video (e.g., names and faces of characters). Thereby, we can more accurately estimate participants and time of a conversation between characters (i.e., a set of connected dialogues). Based on the conversation, the existing character networks are refined and integrated into the unified character network. In addition, we verified the efficacy of the proposed methods using movies in the real world, which are among the most accessible and popular narrative multimedia. © 2019 Elsevier Ltd
- WIMSCharacter network embedding-based plot structure discovery in narrative multimediaO-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Web Intelligence, Mining and Semantics (WIMS 2019) , 2019
This study aims to discover plot structures of narrative multimedia (i.e., creative works that contain stories and are distributed through multimedia). Although a few studies have been conducted to extract subplots from narrative works based on occurrences of characters, the subplots do not always have distinctive compositions of characters. Therefore, we propose a method for discriminating the subplots based on overall social relationships among characters. To understand ways how a story is interwoven with subplots, it is important to describe how story lines in each subplot are developed and how subplots are split and rearranged. As a first step, we propose a measurement for estimating rapidity of story development based on changes in the social relationships among characters. Subsequently, we suggest a model for representing plot structures based on transitions among subplots, the narrative significance of each scene, and the main characters of each subplot. We anticipate that the plot structures can be applied for summarizing narrative multimedia regarding the story. © 2019 ACM.
2018
- IUIwExplainable movie recommendation systems by using story-based similarityO-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the workshop on Explainable Smart Systems (ExSS 2018), held in conjunction with the 23rd International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (IUI 2018) , 2018
The goal of this paper is to provide a story-based explanation for movie recommendation systems, achieved by a multiaspect explanation and narrative analysis methods. We explain how and why particular movies are similar based on following two aspects: (i) composition of movie characters and (ii) interactions among the characters. These aspects correspond to story-based features of the movies that are extracted from character networks (i.e., social networks among the characters). By using the story-based features, we can explain the reason why two arbitrary movies are similar or not. We anticipate that the proposed method could improve the explainability of the recommender systems for movies. © 2018 Copyright for the individual papers remains with the authors.
- MONETOwner-Borrower Model for Recommenders in O2O ServicesO-Joun Lee, and Jai E. JungMobile Networks and Applications, 2018
With remarkable successes of sharing economy services (e.g., UBER (https://www.uber.com), Airbnb (https://www.airbnb.com), and so on), the amount of items which are distributed through these services is rapidly increasing. Therefore recommender systems for the sharing economy services are required. However, the existing recommenders are hard to support the sharing economy services, since they have focused on a ‘Item-User’ model that the recommenders provide satisfiable items to consumers (users) in accordance with only the consumers’ preferences. In this regard, we suggest a novel recommendation model, ‘Owner-Borrower’ model which considers the preferences of both sides: owners and borrowers of properties (items). Also, we propose a recommendation method based on the proposed model by applying a tensor factorization method and the Gale-Shapley algorithm. The tensor factorization is used for estimating preferences of the owners and the borrowers. With the estimated preferences, the Gale-Shapley algorithm makes optimal matches between the borrowers and the owners’ properties. © 2018, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
- JUCSMulti-scaled spatial analytics on discovering latent social events for smart urban servicesO-Joun Lee, Yunhu Kim , Hoang Long Nguyen , and Jai E. JungJournal of Universal Computer Science, 2018
The goal of this paper is to discover latent social events from social media for sensitively understanding social opinions that appeared within a city. The latent social event indicates a regional and inconspicuous social event which is mostly buried under macroscopic trends or issues. To detect the latent social event, we propose three methods: i) discovering areas-of-interest (AOIs), ii) allocating social texts to the AOIs, and iii) detecting social events in each AOI. The AOIs can be composed by grouping social texts which are topically and spatially homogeneous. To make the AOIs dynamic and incremental, we use windows for allocating a social text to an adequate AOI. Lastly, the latent social events are detected from the AOI on the basis of keywords and temporal distribution of the social texts. Although, in this study, we limited the proposed method into analyzing social media, it could be extended to detecting events among agents/things/sensors. © J.UCS.
- CCPESpatio-temporal query contextualization for microtext retrieval in social mediaJae-Hong Park , O-Joun Lee, and Jai E. JungConcurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2018
Generally, texts on the social media (eg, Twitter and Facebook) are too short (microtexts) to understand the meaning and to search for relevant texts. It is difficult for the conventional information retrieval systems to conduct the searching tasks. Thereby, in this paper, we propose a novel approach on query contextualization by integrating all possible microtexts by considering spatio-temporal contexts. The proposed approach consists of two steps, which are (i) to understand and process microtexts in social media and (ii) to reformulate the queries for searching for relevant microtexts in these social media. To evaluate the performance of the query contextualization approach, microtexts from Twitter have been collected during 4 months. © 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- ECIRwMeasuring character-based story similarity by analyzing movie scriptsO-Joun Lee, Nayoung Jo , and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Narrative Extraction From Text (Text2Story 2018), co-located with the 40th European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR 2018) , 2018
The goal of this paper is to measure similarity among the stories for categorizing movies. Although genres are well-performing as movies’ categories, users have difficulty for predicting substances of the movies through the genres. Therefore, we proposed the story-based taxonomy of the movies and a method for constructing it automatically. In order to reflect characteristics of the stories, we used two kinds of features: (i) proximity among movie characters and (ii) genres of the movies. Based on the features, we constructed the story-based taxonomy by clustering the movies. We anticipate that the proposed taxonomy could make the users imagine and predict substances of movies through comprehending which movies contain similar stories. Copyright © 2018 for the individual papers by the paper’s authors.
2017
- IEEE AccessTowards Ontological Approach on Trust-Aware Ambient ServicesO-Joun Lee , Hoang Long Nguyen , Jai E. Jung, Tai-Won Um , and Hyun-Woo LeeIEEE Access, 2017
With various information sources (e.g., from IoT sensors to social media), it is difficult to provide users with trustworthy services in ambient environment. The aim of this paper is i ) to design trust ontology for representing semantics of the ambient services and ii ) to compute trust measures among users by using a personalized trust ontology. In particular, given a large amount of data collected from ambient sensors, efficient trust computation and reasoning are required for the stability and reliability. Thereby, we propose trust ontology-based framework for deriving personalized ontologies for individual users according to their preference, perspective, and purpose. To evaluate the proposed model, we have figured out a method how the degree of trust is estimated based on the trust ontology. Furthermore, we have proved that the proposed method is reliable with a case study on a social media (Twitter) for a particular domain (restaurant). © 2013 IEEE.
- FGCSSequence Clustering-based Automated Rule Generation for Adaptive Complex Event ProcessingO-Joun Lee, and Jai E. JungFuture Generation Computer Systems, 2017
In Complex Event Processing (CEP), complex events are detected according to a set of rules that are defined by domain experts. However, it makes the reliability of the system decreased as dynamic changes occur in the domain environment or domain experts make mistakes. To address such problem, this study proposes a Sequence Clustering-based Automated Rule Generation (SCARG) that can automatically generate rules by mining decision-making history of domain experts based on sequence clustering and probabilistic graphical modeling. Furthermore, based on a two-way learning approach, the proposed method is able to support automated regular or occasional rule updates. It makes self-adaptive CEP system possible by combining the rule generation method and the existing dynamic CEP systems. This technique is verified by establishing an automated stock trading system, and the performance of the system is measured in terms of the rate of return. The study solves the aforementioned problems and shows excellent results with an increase of 19.32% in performance when compared to the existing dynamic CEP technique. © 2016 Elsevier B.V.
- MTAPA computational model of transmedia ecosystem for story-based contentsJai E. Jung , O-Joun Lee, Eun-Soon You, and Myoung-Hee NamMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2017
Story-based contents (e.g., novel, movies, and computer games) have been dynamically transformed into various media. In this environment, the contents are not complete in themselves, but closely connected with each other. Also, they are not simply transformed form a medium to other media, but expanding their stories. It is called as a transmedia storytelling, and a group of contents following it is called as a transmedia ecosystem. Since the contents are highly connected in terms of the story in the transmedia ecosystem, the existing content analysis methods are hard to extract relationships between the contents. Therefore, a proper content analysis method is needed with considering expansions of the story. The aim of this work is to understand how (and why) such contents are transformed by i) defining the main features of the transmedia storytelling and ii) building the taxonomy among the transmedia patterns. More importantly, computational transmedia ecosystem is designed to process a large number of the contents, and to support high understandability of the complex transmedia patterns. © 2016, Springer Science+Business Media New York.
- BDTANetwork engineering: Towards data-driven framework for network configurationKhac Hoai Nam Bui , Sungrae Cho , Jason J. Jung, Joongheon Kim , O-Joun Lee, and Woongsoo NaIn Proceedings of the 8th EAI International Conference on Big Data Technologies and Applications (BDTA 2017) , 2017
In this paper, we want to introduce a new research area “network engineering”. The main research question is how the network configuration can be automatically and adaptively decided, given various dynamic contexts (e.g., network interference, heterogeneity and so on). The aim of this work is to design data-driven framework which is in three layer architecture (i.e., network entity layer, complex semantic analytics layer, and action provisioning layer). © ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 2018.
- IEEE AccessEvent-Driven Trust Refreshment on Ambient ServicesHoang Long Nguyen , O-Joun Lee, Jai E. Jung, Jaehwa Park , Tai-Won Um , and Hyun-Woo LeeIEEE Access, 2017
Since trust among entities can change according to various conditions, it is necessary for ambient services to determine when and how the trust has to be updated. Therefore, our contribution in this paper is to present: 1) a new definition of trust that can be extended to various domains; 2) a novel method based on social events and patterns to trigger trust refreshment in ambient services; and 3) a web application framework (called SocioScope) for collecting and analyzing data from multiple data sources. Finally, the case study suggests that this proposal could be applied to trust-aware ambient and recommendation systems. © 2013 IEEE.
- DaMISSpatio-Temporal Contextualization of Queries for Microtexts in Social Media: Mathematical ModelingJae-Hong Park , O-Joun Lee, Joo-Man Han , Eon-Ji Lee , Jason J. Jung, Luca Carratore , and Francesco PiccialliIn Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop in Data Mining on IoT Systems (DaMIS 2017) held in conjunction with the 8th International Conference on Emerging Ubiquitous Systems and Pervasive Networks (EUSPN 2017) , 2017
In this paper, we present our ongoing project on query contextualization by integrating all possible IoT-based data sources. Most importantly, mobile users are regarded as the IoT sensors which can be the textual data sources with spatio-temporal contexts. Given a large amount of text streams, it has been difficult for the traditional information retrieval systems to conduct the searching tasks. The goal of this work is i) to understand and process microtexts in social media (e.g., Twitter and Facebook), and ii) to reformulate the queries for searching for relevant microtexts in these social media. Peer-review under responsibility of the Conference Program Chairs. © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
- IETowards affective lifelogging with information fusionJason J. Jung, Minsung Hong , O-Joun Lee, Jaehong Park , and Chang ChoiIn Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Intelligent Environments (IE 2017) , 2017
Recently, most of context-aware services are trying to exploit the emotional contexts of the target users. The aim of this conceptual paper is to discuss affective lifelogging framework which can recognize the emotions by integrating multimodal information from multiple sources. Moreover, we will mention the open problems on affective lifelogging. © 2017 IEEE.
- MTAPExploiting character networks for movie summarizationQuang Dieu Tran , Dosam Hwang , O-Joun Lee, and Jai E. JungMultimedia Tools and Applications, 2017
Movie summarization focuses on providing as much information as possible for shorter movie clips while still keeping the content of the original movie and presenting a faster way for the audience to understand the movie. In this paper, we propose a novel method to summarize a movie based on character network analysis and the appearance of protagonist and main characters in the movie. Experiments were carried out for 2 movies (Titanic (1997) and Frozen (2013)) to show that our method outperforms conventional approaches in terms of the movie summarization rate. © 2016, Springer Science+Business Media New York.
2016
- APHAdaptive collaborative filtering based on scalable clustering for big recommender systemsO-Joun Lee, Min-Sung Hong , Jason J. Jung, Juhyun Shin , and Pankoo KimActa Polytechnica Hungarica, 2016
The large amount of information that is currently being collected (the so-called “big data”), have resulted in model-based Collaborative Filtering (CF) methods to encountering limitations, e.g., the sparsity problem and the scalability problem. It is difficult for model-based CF methods to address the scalability-performance trade-off. Therefore, we propose a scalable clustering-based CF method in this paper that can help provide a balance by re-locating elements in the cluster model. The proposed method is evaluated by performing a comparison against existing methods in terms of measurements for the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and response time to assess the performance and scalability. The experimental results show that the proposed method improves the MAE and the response time by 50.79% and 48.25%, respectively. © 2016, Budapest Tech Polytechnical Institution. All rights reserved.
- AfCAIAffective character network for understanding plots of narrative multimedia contentsO-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Affective Computing and Context Awareness in Ambient Intelligence (AfCAI 2016) , 2016
It is important to understand the stories from narrative multimedia contents (e.g., movies), and to exploit the stories for smart services (e.g., video summarization and personalized multimedia recommendation). In this paper, we extend CharNet (Character Network) to Affective CharNet (Affective Character Network) by annotating emotional relationships between characters. More importantly, we propose a novel method on analyzing Affective CharNet for extracting the plots from the narrative multimedia contents. © 2016, CEUR-WS. All rights reserved.
- ISAmIDynamic traffic light control system based on process synchronization among connected vehiclesKhac-Hoai Nam Bui , O-Joun Lee, Jason J. Jung, and David CamachoIn Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ambient Intelligence (ISAmI 2016) , 2016
Vehicular traffic is tremendously increasing around the world, especially in large urban areas. The resulting congestion has become a key issue and emerging research topic to transportation specialist and decision makers. In this study, inspired by recent advanced vehicle technologies, we take into account in improving traffic flow in real-time problem. In order to solve the problem, we propose a new approach to manage traffic flow at the intersection in real-time via controlling by traffic light scheduling. In particular, the proposed method is based on process synchronization theory and connected vehicle technology where each vehicle is able to communicate with others. The traffic deadlock is also taken into consideration in case of high traffic volume. The simulation shows the potential results comparing with the existing traffic management system. © Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2016.
- BDTAA novel method for extracting dynamic character network from movieQuang Dieu Tran , Dosam Hwang , O-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the 7th EAI International Conference on Big Data Technologies and Applications (BDTA 2016) , 2016
In this decade, the number of movies is increasing rapidly. Many studies have been proposed to assist users in movie understanding. In which, these methods are taken into account movie content analysis using social network for discovering relationships among characters and so on. However, these methods have shown some unsatisfactorily in dynamic changing of multimedia contents such as the character’s relationships over time. For overcoming this issue, we proposed a novel method for extracting dynamic character network from a movie. © ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 2017.
2015
- ACIIDSAdaptive complex event processing based on collaborative rule mining engineO-Joun Lee, Eunsoon You, Min-Sung Hong , and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the 7th Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems (ACIIDS 2015) , 2015
Complex Event Processing (CEP) detects complex events or patterns of event sequences based on a set of rules defined by a domain expert. However, it lowers the reliability of a system as the set of rules defined by an expert changes along with dynamic changes in the domain environment. A human error made by an expert is another factor that may undermine the reliability of the system. In an effort to address such problems, this study introduces Collaborative Rule Mining Engine (CRME) designed to automatically mine rules based on the history of decisions made by a domain expert by adopting a collaborative filtering approach, which is effective in mimicking and predicting human decision-making in an environment where there are sufficient data or information to do so. Furthermore, this study suggests an adaptive CEP technique, which does not hamper the reliability since it prevents potential errors caused by mistakes of domain experts and adapts to changes in the domain environment on its own as it is linked to the system proposed by Bharagavi [10]. In a bid to verify this technique, an automated stocks trading system will be established and its performance will be measured using the rate of return. © Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2015.
- ICCASAContext-based traffic recommendation systemKhac-Hoai Nam Bui , Xuan Hau Pham , Jason J. Jung , O-Joun Lee, and Min-Sung HongIn Proceedings of the 5th EAI International Conference on Context-Aware Systems and Applications (ICCASA 2015) , 2015
In this paper, we propose a new traffic system recommendation based on support real-time flows in highly unpredictable sensor network environments. The approach system is real-time recommendation system which meet various demands of users. The proposed algorithm include two phases. First phase is proposed to deal with the real-time problem. By this way, the drivers are able to transfer on the way with the shortest-time. For second phase, a research algorithm based on Depth First Search (DFS) algorithm will recommend the paths which meet demands of drivers based their context such as the paths with include the famous landscapes or the paths where they can find out good restaurants for their break while driving. © ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 2016.
- ICCASAMBTI-based collaborative recommendation system: A case study of Webtoon contentsMyeong-Yeon Yi , O-Joun Lee, and Jason J. JungIn Proceedings of the 5th EAI International Conference on Context-Aware Systems and Applications (ICCASA 2015) , 2015
A large number of Webtoon contents has caused difficulties on finding relevant Webtoons for users. Thereby, an efficient recommendation services are needed. However, since the existing recommendation method (e.g. collaborative filtering) has two fundamental problems: (i.e., data sparsity and scalability problem), it has difficulties with reflecting users’ personality. In this paper, we propose the MBTI-CF method to solve these problems and to involve users’ personality by building personality-based neighborhood using MBTI. In order to verify the efficiency of the proposed method, we conducted statistical testing by user survey (anonymous users have rated set of the pre-selected Webtoon contents). Three experimental results have shown that MBTI-CF provides improvement in terms of the data sparsity problem and the scalability problem and offers more stable performance. © ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 2016.
- CYBCONFPredictive Clustering for performance stability in collaborative filtering techniquesO-Joun Lee, Jason J. Jung, and Eunsoon YouIn Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics (CYBCONF 2015) , 2015
Model-based collaborative filtering improves the fundamental limitations of the collaborative filtering facing the issues of data sparsity and scalability while presenting other constraints of high costs of model building and the tradeoff between performance and scalability. Such tradeoff results in reduced coverage, which is one sort of the sparsity issue. Furthermore, high model building costs lead to unstable performance driven by cumulative changes in the domain environment. To solve these problems, we propose Predictive Clustering-based CF (PCCF) that incorporates the Markov model and fuzzy clustering with Clustering based CF (CBCF). The method improves performance instability by tracking the changes in user preferences and bridging the gap between the static model and dynamic users. Furthermore, the issue of reduced coverage is also improved by expanding the coverage based on transition probabilities. The proposed method has been validated by testing the robustness of performance instability and scalability-performance tradeoff. In comparison with the existing techniques, the suggested method shows slight performance improvement. Notwithstanding, it is more advanced than the existing techniques in terms of the range that indicates the level of performance fluctuation. This signifies that the proposed method, despite the slight performance improvement, clearly offers better performance stability compared to the existing techniques. © 2015 IEEE.
2014
- InformMeta-data configuration and learning technique for wellness content recommendationMin-Sung Hong , O-Joun Lee , Won-Jin Lee , Kee-Won Kim , Seung-Hoon Kim , Hee-Jung Han , and Jae-Dong LeeInformation, 2014
The method for personalized wellness-content recommendation has actively studied in the field of information technology convergence. But a problem with low reliability of recommendations has emerged. Because existing studies deal with only one or two areas of wellness, to solve the reliability problems, a study is needed into an integration technique that can manage several aspects of wellness. In this paper, we propose a metadata configuration and feature analysis technique for integrated management in areas of wellness. And we propose a learning technique for analyzed wellness features using user feedback to increase the reliability of user recommendations. To verify the proposed technique, we compared the results of a pre-survey with those from the proposed technique. © 2014 International Information Institute.